What Are The Later Stages Of Frontotemporal Dementia

As the disease progresses 24-hour care may become necessary.
What are the later stages of frontotemporal dementia. In later stages patients develop movement disorders such as unsteadiness rigidity slowness twitches muscle weakness or difficulty swallowing. People in the final stages of FTD cannot care for themselves. While behavioral changes tend to occur in later stages of Alzheimers they are usually the first.
Severe Behavioral Variant FTD. How Do Alzheimers Disease and Frontotemporal Dementia Differ. Most notably a person will have problems with normal everyday functions like bathing dressing eating and going to the bathroom.
Late-Stage Dementia Eventually your loved one will reach the late stage of dementia also called end-stage dementia or advanced dementia in which symptoms become severe. Frontotemporal dementia FTD a common cause of dementia is a group of disorders that occur when nerve cells in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain are lost. Mild Behavioral Variant With this stage you may notice your loved one is overeating and seems to have a loss of.
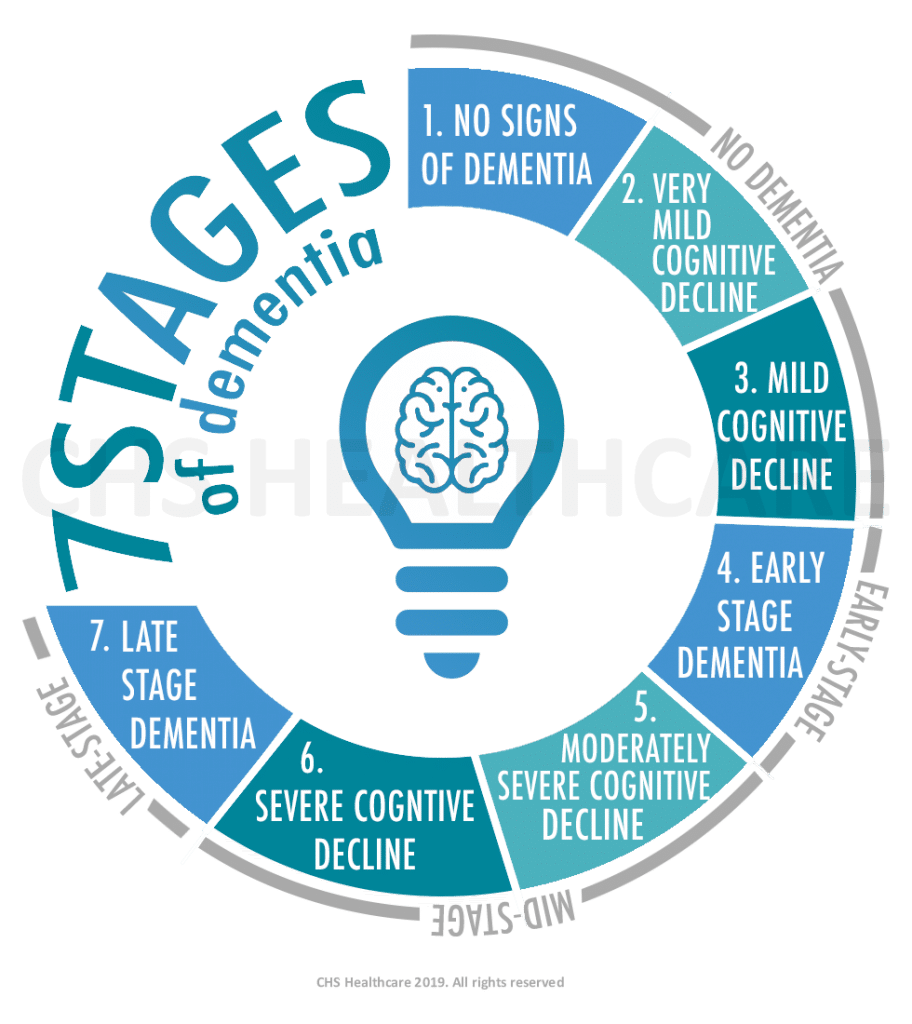
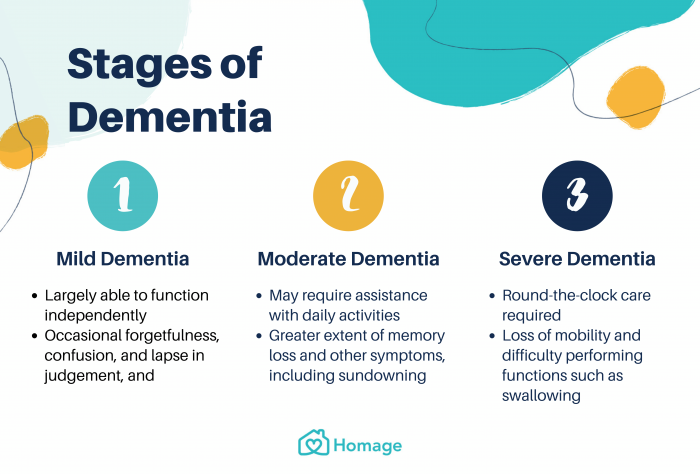
People with FTD tend to struggle with binge eating and compulsive behaviors. In the later stages some people with frontotemporal dementia develop physical problems and difficulties with movement. There are 3 stages of frontotemporal dementia.
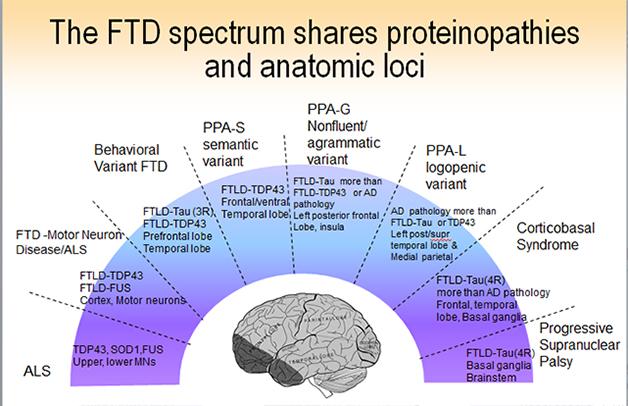
The majority of those with frontotemporal dementia are diagnosed in. In later stages of FTD the clinical phenotypes may overlap. The patient will experience behavioral symptoms that are more profound.
Some patients develop Lou Gherigs disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ALS. This causes the lobes to shrink. Late-stage frontotemporal dementia can take years to develop.

Severe Behavioral Variant FTD.
What are the later stages of frontotemporal dementia. Most notably a person will have problems with normal everyday functions like bathing dressing eating and going to the bathroom. Dementias cognitive problems are more pronounced in moderate FTD. Frontotemporal dementia shortens a persons life span.
There are 3 stages of frontotemporal dementia. How Do Alzheimers Disease and Frontotemporal Dementia Differ. Attention and planning will show deficits and the person will experience forgetfulness and mental rigidity.
People in the final stages of FTD cannot care for themselves. Mild Behavioral Variant With this stage you may notice your loved one is overeating and seems to have a loss of. This causes the lobes to shrink.
Some patients develop Lou Gherigs disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ALS. The patient will experience behavioral symptoms that are more profound. Later stages of the disease - Parkinsonism People in the late stages of FTLD generally experience some physical problems such as stiffness and slowness.
In the later stages some people with frontotemporal dementia develop physical problems and difficulties with movement. Frontotemporal dementia FTD a common cause of dementia is a group of disorders that occur when nerve cells in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain are lost. Late-Stage Dementia Eventually your loved one will reach the late stage of dementia also called end-stage dementia or advanced dementia in which symptoms become severe.
The majority of those with frontotemporal dementia are diagnosed in. In later stages patients develop movement disorders such as unsteadiness rigidity slowness twitches muscle weakness or difficulty swallowing. Late-stage frontotemporal dementia can take years to develop.

This causes the lobes to shrink.
What are the later stages of frontotemporal dementia. People in the final stages of FTD cannot care for themselves. The patient will experience behavioral symptoms that are more profound. In later stages of FTD the clinical phenotypes may overlap.
While behavioral changes tend to occur in later stages of Alzheimers they are usually the first. In later stages patients develop movement disorders such as unsteadiness rigidity slowness twitches muscle weakness or difficulty swallowing. Frontotemporal dementia shortens a persons life span.
Later stages of the disease - Parkinsonism People in the late stages of FTLD generally experience some physical problems such as stiffness and slowness. Mild Behavioral Variant With this stage you may notice your loved one is overeating and seems to have a loss of. Attorneys and financial advisors can help families prepare for the later stages of the disease.
Some patients develop Lou Gherigs disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ALS. Late-stage frontotemporal dementia can take years to develop. How Do Alzheimers Disease and Frontotemporal Dementia Differ.
Attention and planning will show deficits and the person will experience forgetfulness and mental rigidity. Frontotemporal dementia FTD a common cause of dementia is a group of disorders that occur when nerve cells in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain are lost. Most notably a person will have problems with normal everyday functions like bathing dressing eating and going to the bathroom.
Dementias cognitive problems are more pronounced in moderate FTD. In the later stages some people with frontotemporal dementia develop physical problems and difficulties with movement. The majority of those with frontotemporal dementia are diagnosed in.