Is Frontotemporal Dementia A Mental Illness

Frontotemporal dementia often begins between the ages of 40 and 65.
Is frontotemporal dementia a mental illness. 1 However in 40 of FTD cases there is a family history of dementia psychiatric disease andor motor neuron disease and in 10 to 20 of these cases the mutations are autosomal dominant. Of the remaining 10 percent of dementia cases the underlying condition could be one of the following. Frontotemporal dementia usually causes changes in behaviour or language problems at first.
Frontotemporal dementia was significantly misdiagnosed as depression. Dementia is the decrease in mental capacity that is quicker than would be normal with typical maturing. Frontotemporal dementia affects the front and sides of.
Some people also develop physical problems and. Frontotemporal dementia corticobasal degeneration depression -related dementia. These come on gradually and get worse slowly over time.
Signs and Symptoms In the past patients with frontotemporal dementia FTD often were misdiagnosed with depression schizophrenia or Alzheimers disease. But frontotemporal dementia tends to occur at a younger age than does Alzheimers disease. Most cases of FTD are due to mutations that are sporadic spontaneous.
A person suffering from the PSP form of frontotemporal dementia possesses stiffness and awkwardness in gait poor judgment loss of empathy socially inappropriate behavior lack of inhibition repetitive and compulsive behavior inability to concentrate or plan frequent abrupt mood changes speech difficulties problems with balance or movement and memory loss. Frontotemporal dementia FTD a common cause of dementia is a group of disorders that occur when nerve cells in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain are lost. Dementia is the name for problems with mental abilities caused by gradual changes and damage in the brain.
We know that different areas of the brain are responsible for different psychological functions. Frontotemporal dementia primarily influences the frontal and worldly flaps of the mind. Behavioral variant FTD associated with mutations in C9orf72.

Frontotemporal disorders are forms of dementia caused by a family of brain diseases known as frontotemporal lobar degeneration FTLD.
Is frontotemporal dementia a mental illness. Signs and Symptoms In the past patients with frontotemporal dementia FTD often were misdiagnosed with depression schizophrenia or Alzheimers disease. Frontotemporal dementia affects the front and sides of. Behavioral variant FTD associated with mutations in C9orf72.
7 hours agoA single biomarker can accurately indicate the presence of underlying neurodegeneration in people with cognitive issues. Eventually most people will experience problems in both of these areas. 1 However in 40 of FTD cases there is a family history of dementia psychiatric disease andor motor neuron disease and in 10 to 20 of these cases the mutations are autosomal dominant.
These come on gradually and get worse slowly over time. Frontotemporal dementia FTD a common cause of dementia is a group of disorders that occur when nerve cells in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain are lost. A person suffering from the PSP form of frontotemporal dementia possesses stiffness and awkwardness in gait poor judgment loss of empathy socially inappropriate behavior lack of inhibition repetitive and compulsive behavior inability to concentrate or plan frequent abrupt mood changes speech difficulties problems with balance or movement and memory loss.
Frontotemporal dementia was significantly misdiagnosed as depression. Dementia is a severe loss of thinking abilities that interferes with a persons ability to perform daily activities such. Participant education and mental health experience did not influence the identification of dementia.
FTD is often misdiagnosed as a psychiatric disorder most commonly as a mood disorder. Frontotemporal dementia usually causes changes in behaviour or language problems at first. Dementia is the name for problems with mental abilities caused by gradual changes and damage in the brain.
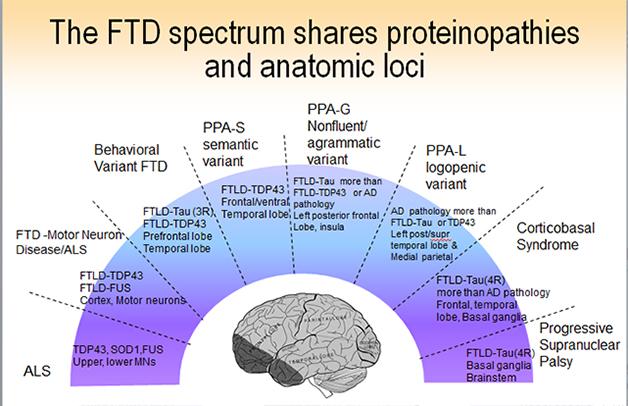
Introduction to frontotemporal dementia FTD is the second most common cause of dementia after Alzheimer disease in the population under age 651 The age of onset is usually between ages 45 and 65 but can range from 30 years to over 80. In general changes in the frontal lobe are associated with behavioral symptoms while changes in the temporal lobe lead to language and emotional disorders. Prevalence is estimated to be about 15 to 22 per 1000002.

These come on gradually and get worse slowly over time.
Is frontotemporal dementia a mental illness. Eventually most people will experience problems in both of these areas. Dementia is the name for problems with mental abilities caused by gradual changes and damage in the brain. Some people also develop physical problems and.
But frontotemporal dementia tends to occur at a younger age than does Alzheimers disease. Dementia is the decrease in mental capacity that is quicker than would be normal with typical maturing. Frontotemporal dementia corticobasal degeneration depression -related dementia.
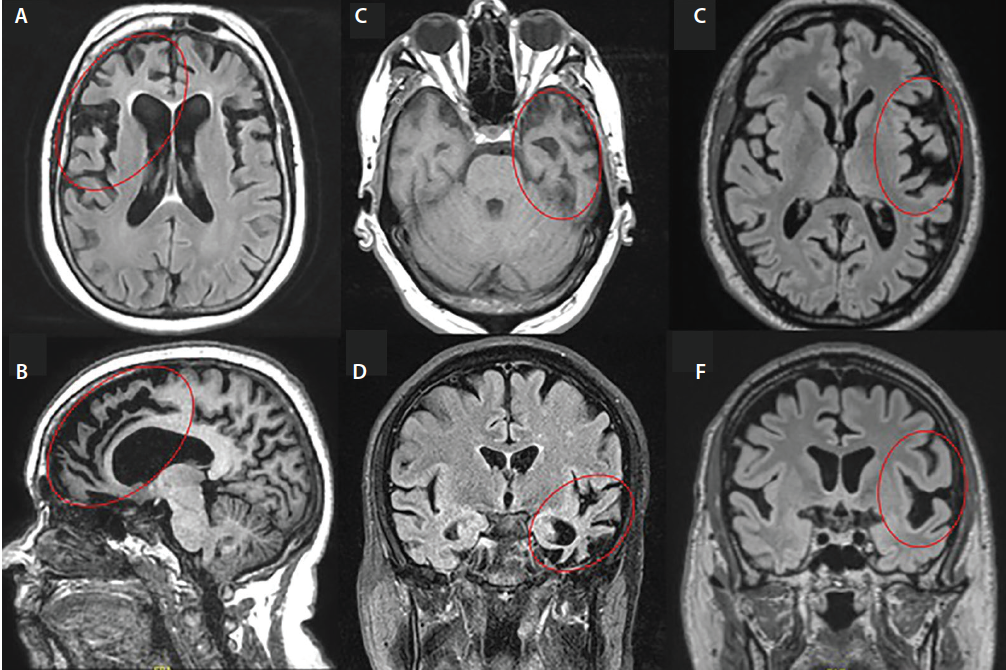
Of the remaining 10 percent of dementia cases the underlying condition could be one of the following. Symptoms of frontotemporal disorders vary from person to person and from one stage of the disease to the next as different parts of the frontal and temporal lobes are affected. Frontotemporal dementia was significantly misdiagnosed as depression.
We know that different areas of the brain are responsible for different psychological functions. Frontotemporal dementia FTD a common cause of dementia is a group of disorders that occur when nerve cells in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain are lost. A person suffering from the PSP form of frontotemporal dementia possesses stiffness and awkwardness in gait poor judgment loss of empathy socially inappropriate behavior lack of inhibition repetitive and compulsive behavior inability to concentrate or plan frequent abrupt mood changes speech difficulties problems with balance or movement and memory loss.
7 hours agoA single biomarker can accurately indicate the presence of underlying neurodegeneration in people with cognitive issues. Frontotemporal dementia primarily influences the frontal and worldly flaps of the mind. Prevalence is estimated to be about 15 to 22 per 1000002.
Introduction to frontotemporal dementia FTD is the second most common cause of dementia after Alzheimer disease in the population under age 651 The age of onset is usually between ages 45 and 65 but can range from 30 years to over 80. Behavioral variant FTD associated with mutations in C9orf72. These disorders are among the most common dementias that strike at younger ages.