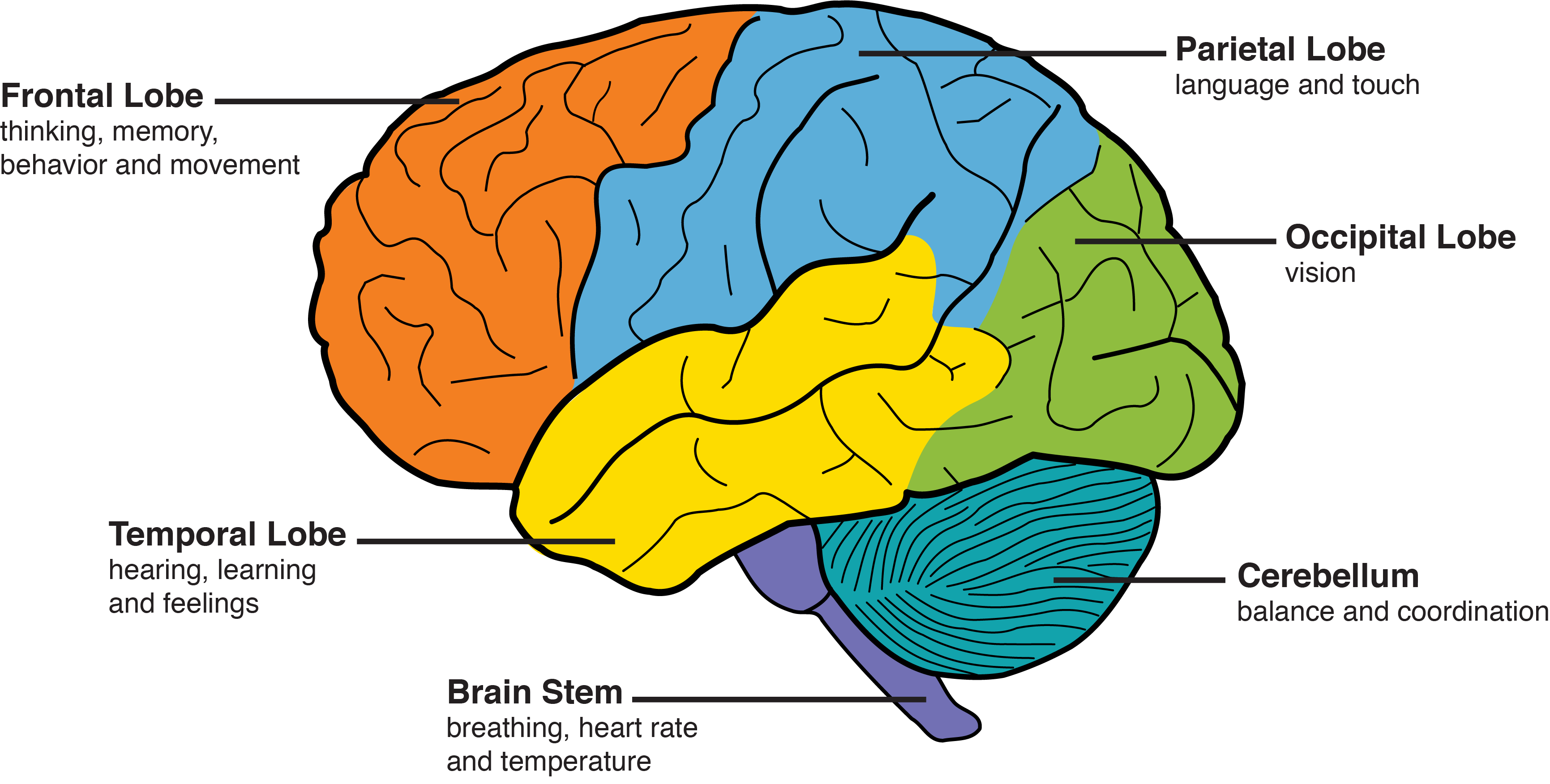
Frontal Lobe Dementia Symptoms Alcohol

Alcohol-related alcoholic dementia also known as Korsakoffs Syndrome is characterized by amnesia volatile mood changes and balance problems that can lead to falls and head injuries.
Frontal lobe dementia symptoms alcohol. Motor neurone disease causes increasing weakness usually with muscle wasting corticobasal degeneration causes problems controlling limbs loss of balance and co-ordination slowness and reduced mobility. Catherine Fortier a clinical neuropsychologist at Harvard Medical School has found reduced gray matter or nerve cells across the entire brain in that group. For example headaches frequent anger episodes mood swings slurred speech as well as memory gaps are serious signs of alcoholic dementia.
Researchers found that older adults who engaged in binge drinking once per month were 62 percent more likely to experience declines in cognitive function while 27 percent experienced the greatest declines in cognitive function. Profound changes in personality. Long-term intake of excessive alcohol causes various forms of brain dam-age most of which are now visualized by magnetic resonance imaging MRI and proved to be contributing to the early onset of dementia.
Other symptoms consistent with dysfunction of the frontal lobes can include problems with short-term memory planning problem solving impulsivity disinhibition and poor motivation Krans and Maki 1997. Bi-frontal atrophy has a unique position among these various forms of damage. A lcohol-related dementia is characterized by impaired executive functioning planning thinking and judgment.
Other features of alcohol-related dementia include. At the end of the course of the disease the persons speech becomes even more monotonous. Deficits with attention concentration and memory.
Alcohol Consumption after Dementia An English study examined people who already had dementia and found that alcohol consumption increased the likelihood of their decline. But we now know that the brains frontal lobes are actually damaged by alcohol at an. Common symptoms can include.
Such symptoms would increase the risk of engagement in and exposure to acts of violence and criminal activities carrying a risk. After all a diagnosis of dementia relies on memory loss. Fixed mood and behaviour appearing selfish and unable to adapt to new situations Loss of empathy emotional warmth and emotional responses Apathy or lack of motivation abandoning hobbies or avoiding social contact Loss of normal inhibitions talking to strangers or.

Frontal lobe deficiency characterized by executive dysfunction such as deficits in attention and working memory has been linked with an inability to abstain from alcohol.
Frontal lobe dementia symptoms alcohol. Fixed mood and behaviour appearing selfish and unable to adapt to new situations Loss of empathy emotional warmth and emotional responses Apathy or lack of motivation abandoning hobbies or avoiding social contact Loss of normal inhibitions talking to strangers or. Alcohol Consumption after Dementia An English study examined people who already had dementia and found that alcohol consumption increased the likelihood of their decline. Common symptoms can include.
Alcoholics often develop personality and behavioural changes social and personal neglect confabulation lack of insight empathy and emotional control. At the end of the course of the disease the persons speech becomes even more monotonous. Motor neurone disease causes increasing weakness usually with muscle wasting corticobasal degeneration causes problems controlling limbs loss of balance and co-ordination slowness and reduced mobility.
Sudden outbursts of rage and excessive alcohol consumption may occur. After all a diagnosis of dementia relies on memory loss. For example headaches frequent anger episodes mood swings slurred speech as well as memory gaps are serious signs of alcoholic dementia.
Long-term intake of excessive alcohol causes various forms of brain dam-age most of which are now visualized by magnetic resonance imaging MRI and proved to be contributing to the early onset of dementia. Catherine Fortier a clinical neuropsychologist at Harvard Medical School has found reduced gray matter or nerve cells across the entire brain in that group. Researchers found that older adults who engaged in binge drinking once per month were 62 percent more likely to experience declines in cognitive function while 27 percent experienced the greatest declines in cognitive function.
A lcohol-related dementia is characterized by impaired executive functioning planning thinking and judgment. Other features of alcohol-related dementia include. Most of the work on how alcohol damages the brain has been done in recovering alcoholics.
Deficits with attention concentration and memory. But we now know that the brains frontal lobes are actually damaged by alcohol at an. Such symptoms would increase the risk of engagement in and exposure to acts of violence and criminal activities carrying a risk.

Alcoholics often develop personality and behavioural changes social and personal neglect confabulation lack of insight empathy and emotional control.
Frontal lobe dementia symptoms alcohol. Long-term intake of excessive alcohol causes various forms of brain dam-age most of which are now visualized by magnetic resonance imaging MRI and proved to be contributing to the early onset of dementia. Alcohol Consumption after Dementia An English study examined people who already had dementia and found that alcohol consumption increased the likelihood of their decline. Bi-frontal atrophy has a unique position among these various forms of damage.
Sudden outbursts of rage and excessive alcohol consumption may occur. After all a diagnosis of dementia relies on memory loss. Having regular alcohol blackout symptoms while drinking is also dangerous to the human brain and acts as a contributing factor to this condition.
Researchers found that older adults who engaged in binge drinking once per month were 62 percent more likely to experience declines in cognitive function while 27 percent experienced the greatest declines in cognitive function. Deficits with attention concentration and memory. Motor neurone disease causes increasing weakness usually with muscle wasting corticobasal degeneration causes problems controlling limbs loss of balance and co-ordination slowness and reduced mobility.
At the end of the course of the disease the persons speech becomes even more monotonous. But we now know that the brains frontal lobes are actually damaged by alcohol at an. Other features of alcohol-related dementia include.
Catherine Fortier a clinical neuropsychologist at Harvard Medical School has found reduced gray matter or nerve cells across the entire brain in that group. Such symptoms would increase the risk of engagement in and exposure to acts of violence and criminal activities carrying a risk. Common symptoms can include.
Most of the work on how alcohol damages the brain has been done in recovering alcoholics. Other symptoms consistent with dysfunction of the frontal lobes can include problems with short-term memory planning problem solving impulsivity disinhibition and poor motivation Krans and Maki 1997. For example headaches frequent anger episodes mood swings slurred speech as well as memory gaps are serious signs of alcoholic dementia.