How Long Does Someone Live With Frontal Lobe Dementia
People are also at increased risk for infections and fall-related injuries.
How long does someone live with frontal lobe dementia. Once a patient begins experiencing any of the above symptoms it is time to speak with a hospice professional about how. A person with frontotemporal dementia usually lives between six to eight years after diagnosis though some will hold on longer. The cause of death is not the illness itself but complications from its symptoms.
There is no one test that will determine if someone has it or not. Pneumonia is the most common cause of death with FTD. But it can lead to an increased risk for other illnesses that can be more serious.
Stage 1 of dementia can also be classified as the normal functioning stage. Stages 1-3 of dementia progression are generally known as pre-dementia stages. Age Associated Memory Impairment.
This is a progressive disease in which the symptoms tend to worsen each year eventually requiring 24-hour assistance. FTD is the diagnosis for about 5 percent of people with major neurocognitive disorders dementia. FTD is not life-threatening people may live with it for years.
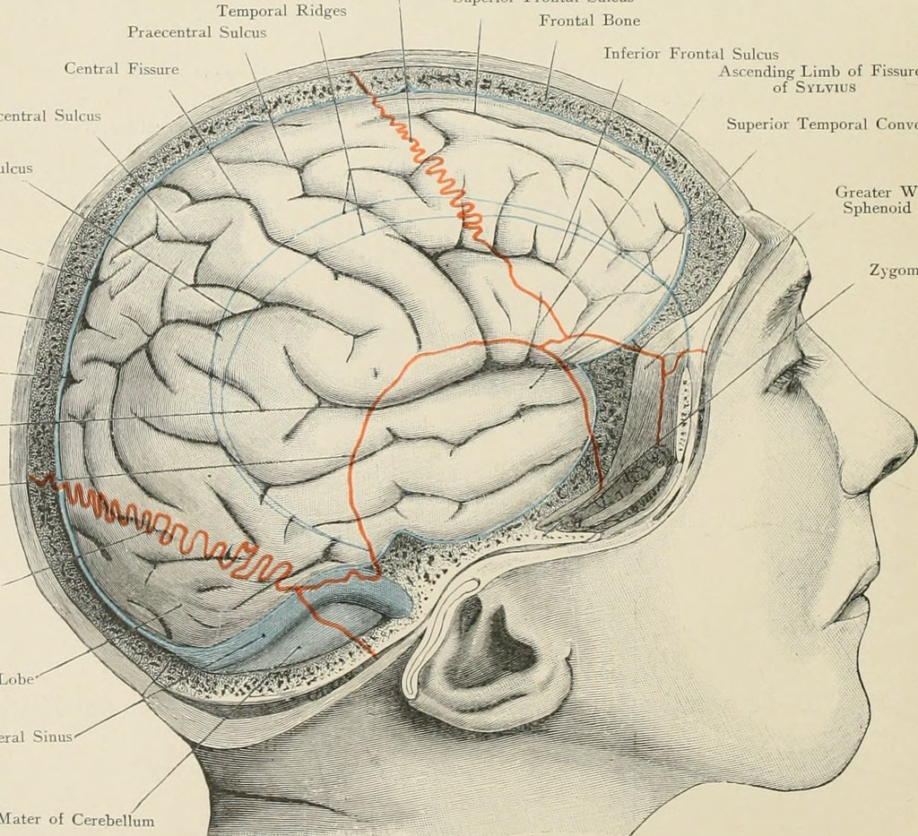
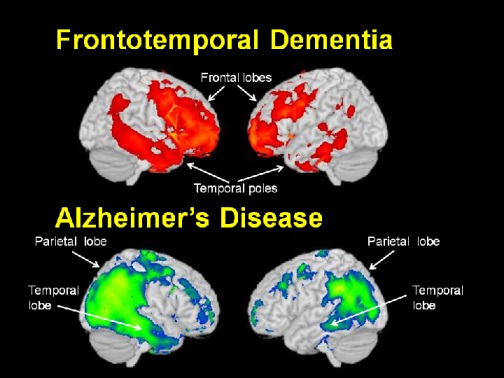
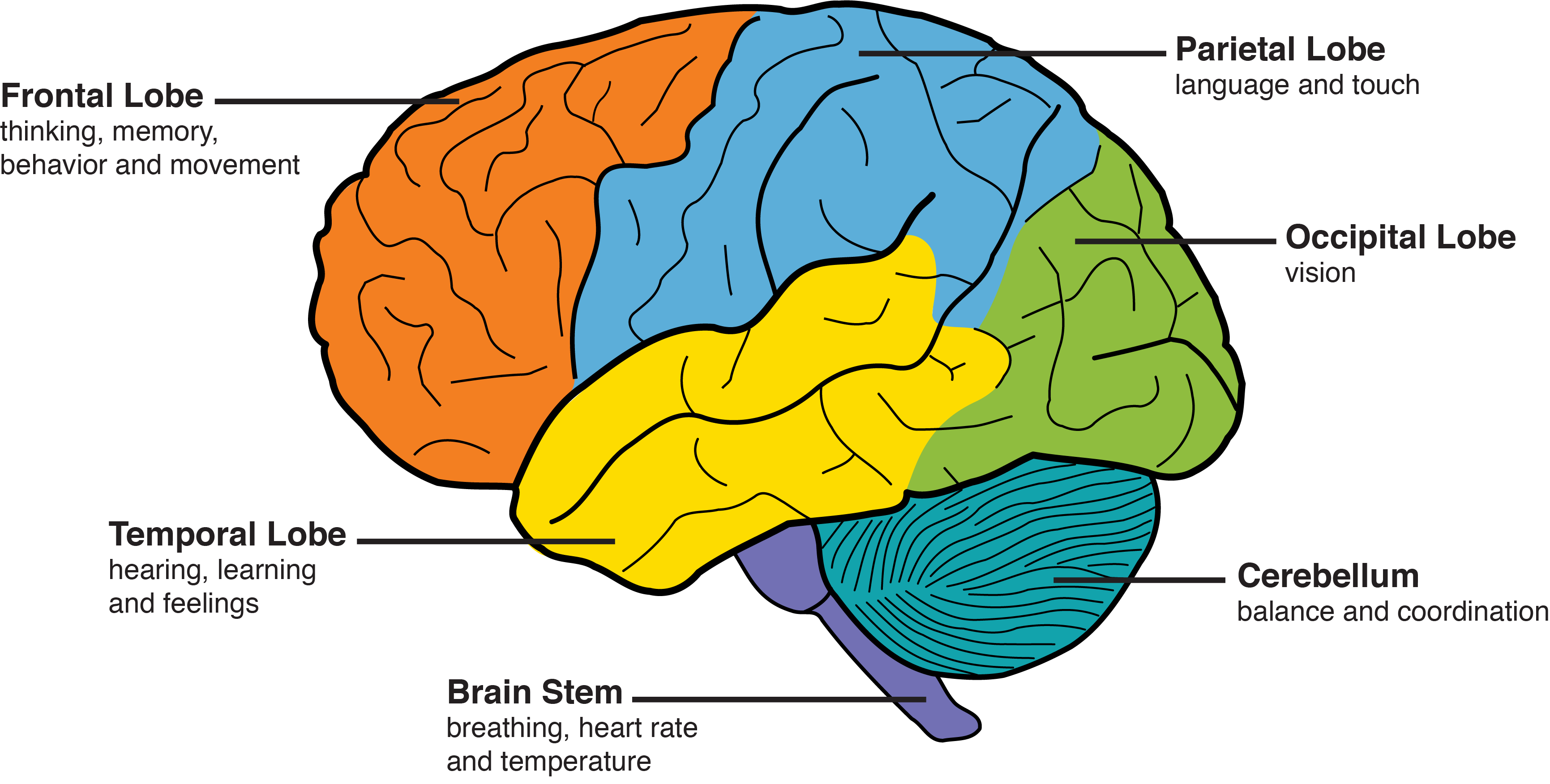
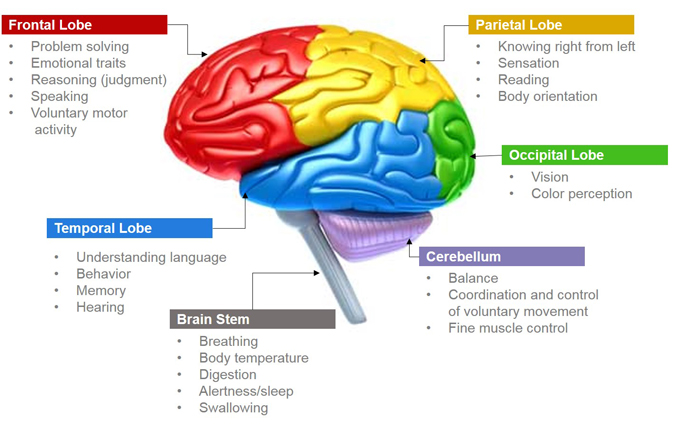
About 70 percent of cases begin before age 65 so it is a more common dementia among the young old FTD involves degeneration of the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. Patients with dementia are eligible to receive hospice care if they have a diagnosis of six months or less to live if the disease progresses in a typical fashion. How to Diagnose Frontotemporal Dementia Because frontotemporal dementia can start at an earlier age it can be difficult to diagnose.
Dementia life expectancy is a measure of how long an average individual is expected to live after developing dementia. Do Treatments Add Time to Life Expectancy. People with young-onset dementia live an average of 10 years with the disease.

For instance a person may die from an infection like aspiration pneumonia which occurs as a result of swallowing difficulties or a person may die from a blood clot in the lung as a result of being immobile and bedbound.
How long does someone live with frontal lobe dementia. There is no one test that will determine if someone has it or not. The cause of death is not the illness itself but complications from its symptoms. On the average an individual diagnosed with dementia resulting from Alzheimers disease will live 45 years beyond the diagnosis.
Stages 1-3 of dementia progression are generally known as pre-dementia stages. A person with frontotemporal dementia usually lives between six to eight years after diagnosis though some will hold on longer. Age Associated Memory Impairment.
FTD often strikes people in the prime of their lives when theyre working and raising families. FTD is the diagnosis for about 5 percent of people with major neurocognitive disorders dementia. The frontal lobe dementia life expectancy can be as long as seventeen years but some patients only live two years as they soon succumb to complications of the disease.
On average an individual with Alzheimers disease lives four to eight years after being diagnosed but can live as long as 20 years according to the Alzheimers Association. Do Treatments Add Time to Life Expectancy. Stage 1 of dementia can also be classified as the normal functioning stage.
In the end most people with late-stage dementia die of a medical complication related to their underlying dementia. Persons can live with frontotemporal disorders for two to 10 years. People with young-onset dementia live an average of 10 years with the disease.
Most people die of problems related to advanced disease. But it can lead to an increased risk for other illnesses that can be more serious. At this stage of dementia development a patient generally does not exhibit any significant problems with memory or any cognitive impairment.

This is a progressive disease in which the symptoms tend to worsen each year eventually requiring 24-hour assistance.
How long does someone live with frontal lobe dementia. The frontal lobe dementia life expectancy can be as long as seventeen years but some patients only live two years as they soon succumb to complications of the disease. Do Treatments Add Time to Life Expectancy. FTD is the diagnosis for about 5 percent of people with major neurocognitive disorders dementia.
At this stage of dementia development a patient generally does not exhibit any significant problems with memory or any cognitive impairment. Most people die of problems related to advanced disease. Patients with dementia are eligible to receive hospice care if they have a diagnosis of six months or less to live if the disease progresses in a typical fashion.
On the average an individual diagnosed with dementia resulting from Alzheimers disease will live 45 years beyond the diagnosis. A person with frontotemporal dementia usually lives between six to eight years after diagnosis though some will hold on longer. Once a patient begins experiencing any of the above symptoms it is time to speak with a hospice professional about how.
What are the complications of frontotemporal dementia. Experts simply dont know whether treatments help a person live longer with Alzheimers disease. Stages 1-3 of dementia progression are generally known as pre-dementia stages.
About 70 percent of cases begin before age 65 so it is a more common dementia among the young old FTD involves degeneration of the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. Even so when it comes to how long can a person live with frontotemporal dementia it is typically between 6 and 8 years once the symptoms start. There is no one test that will determine if someone has it or not.
Frontal lobe dementia is distinguished from other types of dementia by the presence of abnormalities in the nerve cells of the brain known as Pick bodies. On average an individual with Alzheimers disease lives four to eight years after being diagnosed but can live as long as 20 years according to the Alzheimers Association. But it can lead to an increased risk for other illnesses that can be more serious.