Frontal Lobe Syndrome And Frontotemporal Dementia

The Frontal Assessment Battery FAB has been found to have good reliability in identifying an executive.
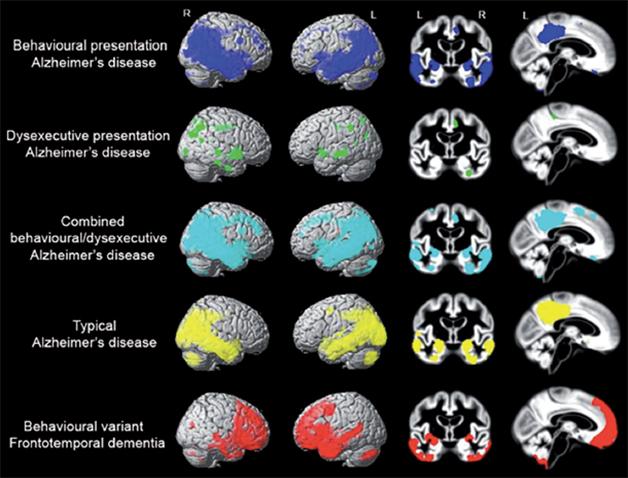
Frontal lobe syndrome and frontotemporal dementia. Frontotemporal dementia FTD primary progressive aphasia PPA corticobasal degeneration syndrome CBS and progressive supranuclear palsy syndrome PSPS. Although the pathological hallmarks of Alzheimers disease AD and frontal variant frontotemporal dementia fvFTD predict different cognitive patterns many comparative neuropsychological studies showed no difference in the expected cognitive domains. About 3040 of cases diagnosed with FTD.
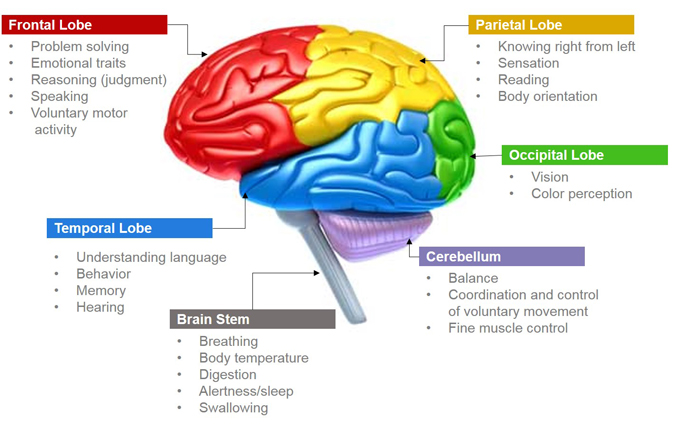
The symptoms and signs of the disease can vary depending on which part of the brain is impacted. Frontotemporal dementia affects the front and sides of the brain the frontal and temporal lobes. About 70 percent of cases begin before age 65 so it is a more common dementia among the young old FTD involves degeneration of the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain.
As neurons die in the frontal and temporal regions these lobes atrophy or shrink. Dementia mostly affects people over 65 but frontotemporal dementia tends to start at a younger age. Frontotemporal dementia includes two distinct conditions.
Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration FTLD is the neuropathological term for a collection of rare neurodegenerative diseases that correspond to four main overlapping clinical syndromes. The prevalence of frontal variant frontotemporal dementia and the frontal lobe syndrome in a population based sample of 85 year olds. FTD is the diagnosis for about 5 percent of people with major neurocognitive disorders dementia.
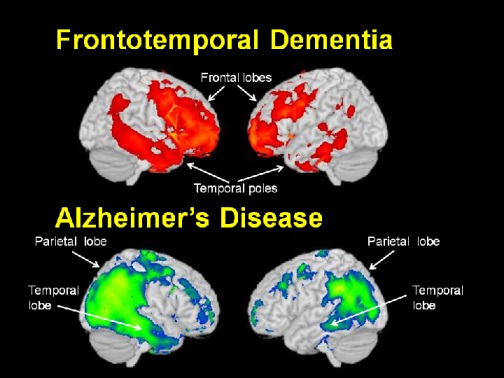
An early differentiation of Alzheimers disease AD from frontotemporal dementia FTD is important since these conditions are essentially different regarding prognosis and therapeutical approach. It affects 5 to 15 percent of people with dementia. Some people have frontotemporal dementia overlapping with other neurological nerve and brain problems including.
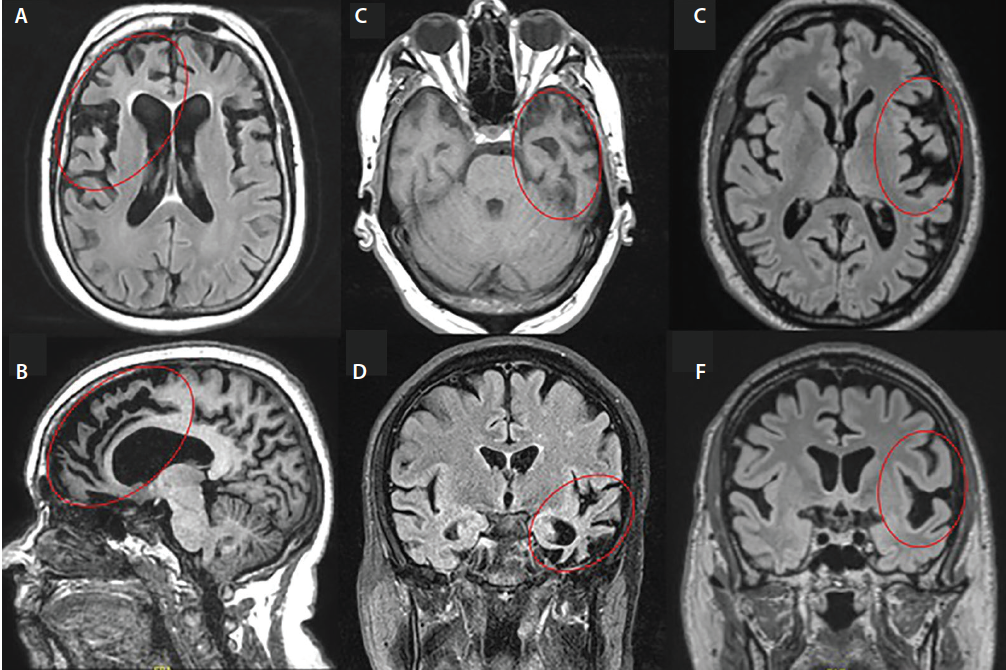
Once damaged the nerve cells shrink atrophy. The Institute of Clinical Neuroscience Department of Psychiatry Sahlgrenska Hospital Gothenburg Sweden. Youve probably heard of Alzheimers disease.

It affects 5 to 15 percent of people with dementia.
Frontal lobe syndrome and frontotemporal dementia. Although the pathological hallmarks of Alzheimers disease AD and frontal variant frontotemporal dementia fvFTD predict different cognitive patterns many comparative neuropsychological studies showed no difference in the expected cognitive domains. Some people have frontotemporal dementia overlapping with other neurological nerve and brain problems including. Frontotemporal dementia includes two distinct conditions.
Frontotemporal dementia FTD is a type of dementia that happens because of damage to the frontal and temporal lobes of your brain. One of these more specific types is frontotemporal dementia FTD a disorder that affects the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain located at the front and lower sides of the brain. Frontotemporal dementia affects the front and sides of the brain the frontal and temporal lobes.
An early differentiation of Alzheimers disease AD from frontotemporal dementia FTD is important since these conditions are essentially different regarding prognosis and therapeutical approach. Motor neurone disease causes increasing weakness usually with muscle wasting corticobasal degeneration causes problems controlling limbs loss of balance and co-ordination slowness and reduced mobility. Frontotemporal dementia is the result of damaged nerve cells in the temporal and frontal lobes.
Until now no single test is available which allows a reliable differentiation. The prevalence of frontal variant frontotemporal dementia and the frontal lobe syndrome in a population based sample of 85 year olds. Once damaged the nerve cells shrink atrophy.
As neurons die in the frontal and temporal regions these lobes atrophy or shrink. T Gislason M Sjogren L Larsson and I Skoog. Frontotemporal disorders are the result of damage to neurons nerve cells in parts of the brain called the frontal and temporal lobes.
Most cases are diagnosed in people aged 45-65 although it can also affect younger or older people. Inconsistencies in diagnostic criteria small cohorts of patients and neuropsychological assessment may account for such findings. It may be the most.
Motor neurone disease causes increasing weakness usually with muscle wasting corticobasal degeneration causes problems controlling limbs loss of balance and co-ordination slowness and reduced mobility.
Frontal lobe syndrome and frontotemporal dementia. About 3040 of cases diagnosed with FTD. Frontotemporal dementia FTD primary progressive aphasia PPA corticobasal degeneration syndrome CBS and progressive supranuclear palsy syndrome PSPS. The nerve cell damage leads to loss of function in these brain regions which can variably cause deterioration in.
Youve probably heard of Alzheimers disease. Frontotemporal dementia includes two distinct conditions. FTD is the diagnosis for about 5 percent of people with major neurocognitive disorders dementia.
Some people have frontotemporal dementia overlapping with other neurological nerve and brain problems including. Picks disease and corticobasal degeneration. The prevalence of frontal variant frontotemporal dementia and the frontal lobe syndrome in a population based sample of 85 year olds.
Until now no single test is available which allows a reliable differentiation. Frontotemporal dementia affects the front and sides of the brain the frontal and temporal lobes. About 70 percent of cases begin before age 65 so it is a more common dementia among the young old FTD involves degeneration of the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain.
An early differentiation of Alzheimers disease AD from frontotemporal dementia FTD is important since these conditions are essentially different regarding prognosis and therapeutical approach. One of these more specific types is frontotemporal dementia FTD a disorder that affects the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain located at the front and lower sides of the brain. Although the pathological hallmarks of Alzheimers disease AD and frontal variant frontotemporal dementia fvFTD predict different cognitive patterns many comparative neuropsychological studies showed no difference in the expected cognitive domains.
Dementia mostly affects people over 65 but frontotemporal dementia tends to start at a younger age. Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration FTLD is the neuropathological term for a collection of rare neurodegenerative diseases that correspond to four main overlapping clinical syndromes. As neurons die in the frontal and temporal regions these lobes atrophy or shrink.