Does Frontal Lobe Damage Affect Memory

Damage to the frontal lobe can cause increased irritability which may include a change in mood and an inability to regulate behavior.
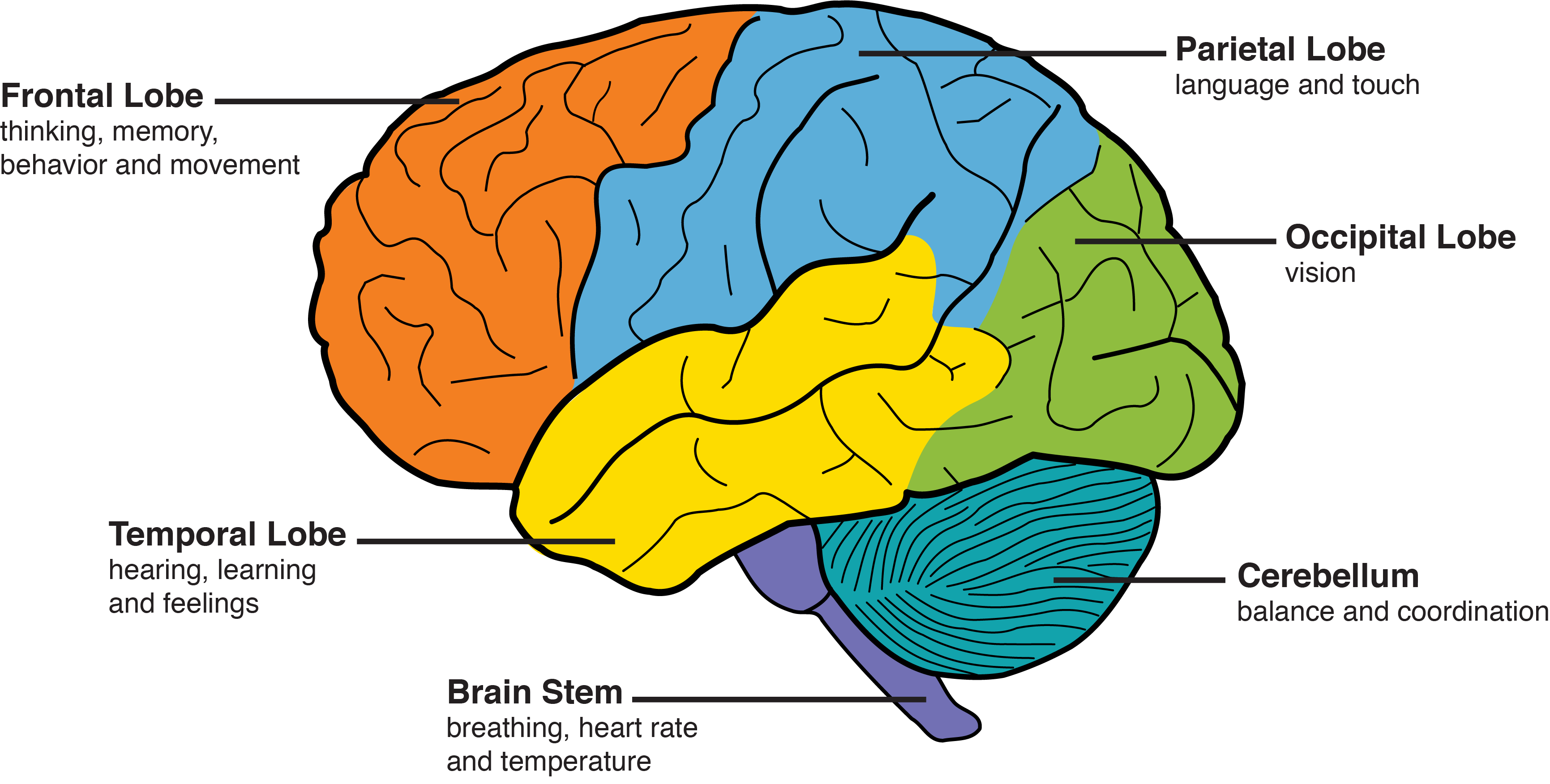
Does frontal lobe damage affect memory. The frontal lobe is the part of the brain that controls cognitive skills of the body. One of the two parietal lobes of the brain located behind the frontal lobe at the top of the brain. Frontal Lobe Damage According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke the frontal lobe plays an important role in planning attention memory and executive functioning.
It is in essence the control panel of our personality and our ability to communicate. Does frontal lobe damage affect memory. Frontal lobe damage results in drastic behavioral and.
The damage to the brain may still be serious if the impact caused bleeding or tearing of any of the nerves and tissues. These cognitive skills include the emotions memory problem solving skills judgment language and sexual behavior. Some researchers are now trying to place certain functions with greater specificity within the frontal lobes.
An injury stroke infection or neurodegenerative disease most often causes damage to the frontal. Frontal lobe injuries can greatly affect a persons ability to pay attention and can even make it difficult for them to form long-term memories. Secondly the memory deficits produced by frontal lesions tend to be subtle and it is likely that the sorts of memory processes subserved by FC are some distance upstream of observed behaviours Burgess 1997.
If the frontal lobes are heavily involved in the organization of information it follows that memory tests that require more organization of material should be affected by dysfunctioning of the frontal lobes. Any damages on the frontal lobe can also impair complex movements such as preparing coffee. Damage to the frontal lobe can spur sudden and immediate alterations in personality.
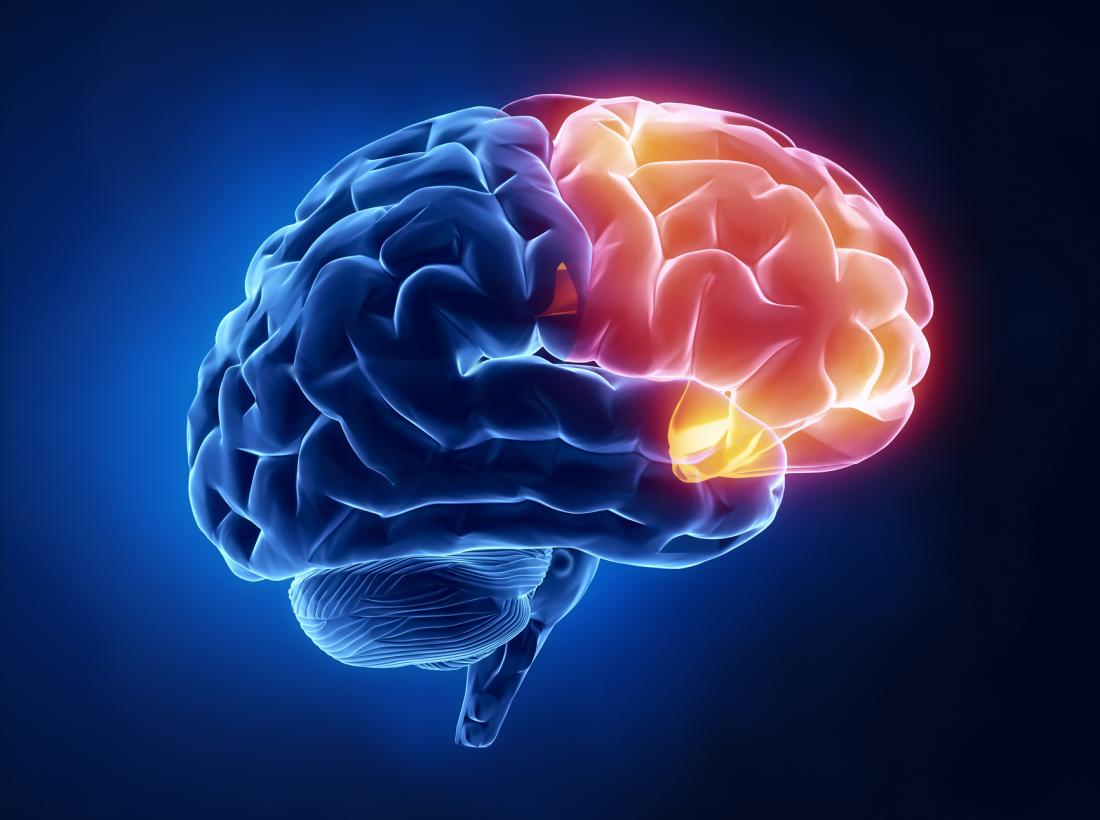
If there is serious bleeding that leads to pressure on the brain surgery may be needed to stop the bleed and remove the blood. The frontal lobe is divided into a left and a right hemisphere. Damage to this lobe can cause visual deficits.

Damage to this lobe can cause visual deficits.
Does frontal lobe damage affect memory. Secondly the memory deficits produced by frontal lesions tend to be subtle and it is likely that the sorts of memory processes subserved by FC are some distance upstream of observed behaviours Burgess 1997. 2 People with FTD usually present with behavior and personality changes andor aphasia language difficulties. Frontotemporal disorders affect the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain.
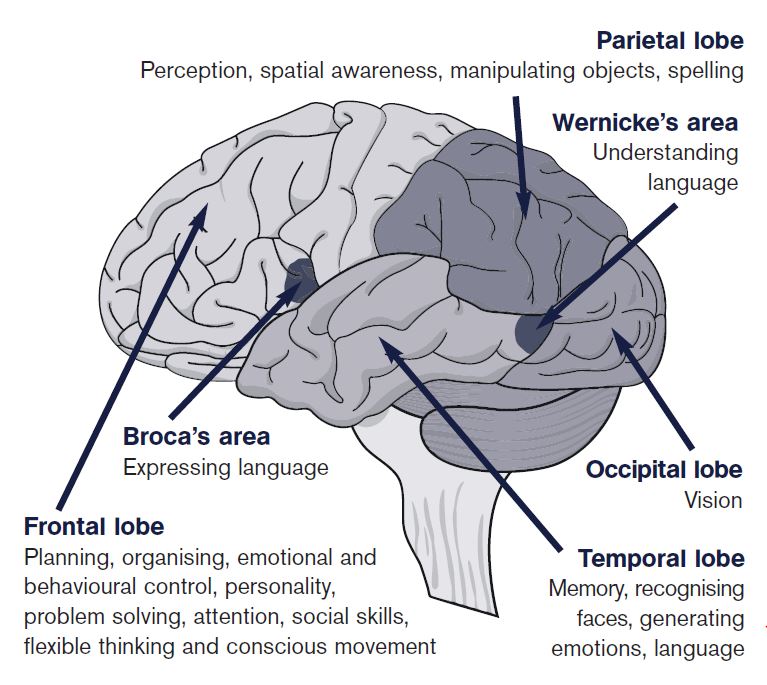
If there is serious bleeding that leads to pressure on the brain surgery may be needed to stop the bleed and remove the blood. Parietal Lobe Right - Damage to this area can cause visuo-spatial deficits eg the patient may have difficulty finding their way around new or even familiar places. If the frontal lobes are heavily involved in the organization of information it follows that memory tests that require more organization of material should be affected by dysfunctioning of the frontal lobes.
The frontal lobe is divided into a left and a right hemisphere. The damage to the brain may still be serious if the impact caused bleeding or tearing of any of the nerves and tissues. One of the two parietal lobes of the brain located behind the frontal lobe at the top of the brain.
Any damages on the frontal lobe can also impair complex movements such as preparing coffee. An injury stroke infection or neurodegenerative disease most often causes damage to the frontal. Does frontal lobe damage affect memory.
The frontal lobe plays an important role in brain functions such as voluntary under conscious control movements memory problem-solving speech and performing everyday tasks which involve multiple steps. Both of those hemispheres or lobes determine who you are through your personality and emotions. The frontal lobes situated above the eyes and behind the forehead on the right and left sides of the brain direct executive functioning.
Some researchers are now trying to place certain functions with greater specificity within the frontal lobes. Click to see full answer. Damage to the frontal lobes can affect one or more of the functions of this area of your brain.

A closed frontal lobe injury means that the skull was not broken or punctured.
Does frontal lobe damage affect memory. Memory impairment is another common effect associated with frontal lobe injuries but this effect is less documented and may or may not be the result of flawed testing. 2 People with FTD usually present with behavior and personality changes andor aphasia language difficulties. The frontal lobe is divided into a left and a right hemisphere.
Damage to the frontal lobe can spur sudden and immediate alterations in personality. If there is serious bleeding that leads to pressure on the brain surgery may be needed to stop the bleed and remove the blood. It is in essence the control panel of our personality and our ability to communicate.
Secondly the memory deficits produced by frontal lesions tend to be subtle and it is likely that the sorts of memory processes subserved by FC are some distance upstream of observed behaviours Burgess 1997. Click to see full answer. Some researchers are now trying to place certain functions with greater specificity within the frontal lobes.
In this manner how does the frontal lobe affect memory. People with frontal lobe damage often struggle with gathering information remembering previous experiences and making decisions based on this input. Damage to the frontal lobes can affect one or more of the functions of this area of your brain.
Parietal Lobe Right - Damage to this area can cause visuo-spatial deficits eg the patient may have difficulty finding their way around new or even familiar places. Frontal lobe injuries can greatly affect a persons ability to pay attention and can even make it difficult for them to form long-term memories. Does frontal lobe damage affect memory.
The frontal lobe is the part of the brain that controls cognitive skills of the body. An injury stroke infection or neurodegenerative disease most often causes damage to the frontal. One of the two parietal lobes of the brain located behind the frontal lobe at the top of the brain.