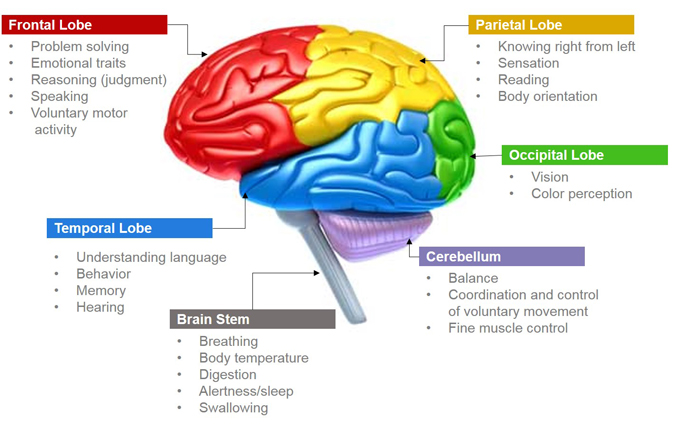
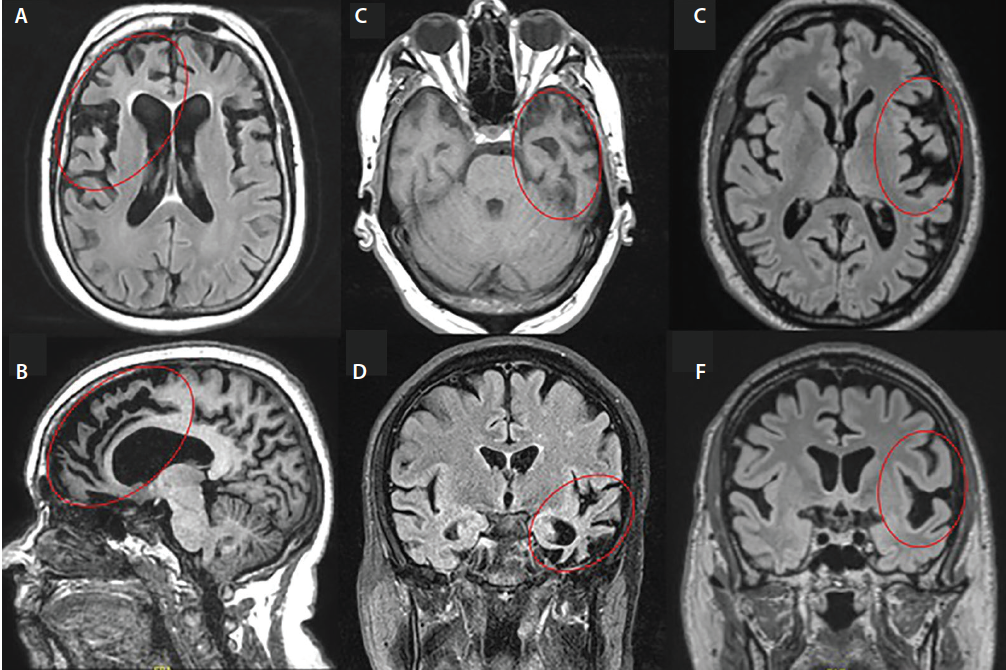
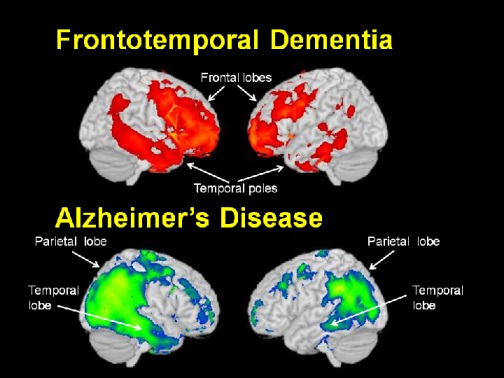
Frontal Lobe Syndrome Frontotemporal Dementia

FTD can affect behavior personality language and movement.
Frontal lobe syndrome frontotemporal dementia. This causes the lobes to shrink. In general changes in the frontal lobe are associated with behavioral symptoms while changes in the temporal lobe lead to language and emotional disorders. Symptoms include marked changes in social behavior and personality andor problems with language.
In this section you will learn the essential facts about FTD. FTD is the diagnosis for about 5 percent of people with major neurocognitive disorders dementia. Frontotemporal disorders are forms of dementia caused by a family of brain diseases known as frontotemporal lobar degeneration FTLD.
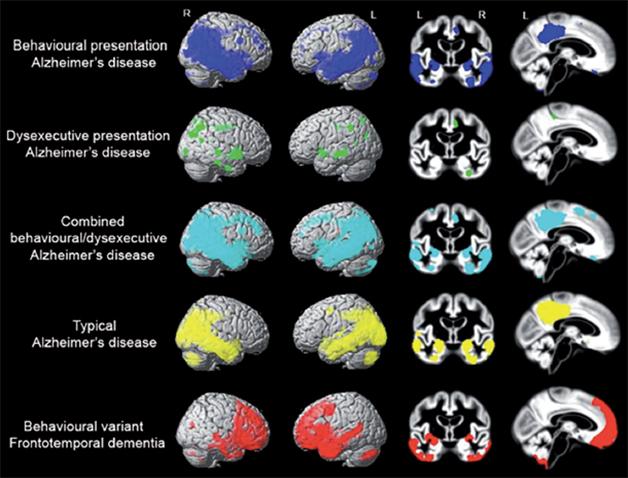
These disorders are among the most common dementias that strike at younger ages. Its the most common dementia for those under 60 yet its widely misunderstood and too often misdiagnosed. An early differentiation of Alzheimers disease AD from frontotemporal dementia FTD is important since these conditions are essentially different regarding prognosis and therapeutical approach.
Symptoms of frontotemporal disorders vary from person to person and from one stage of the disease to the next as different parts of the frontal and temporal lobes are affected. To investigate the prevalence of the frontal lobe syndrome FLS and the frontal variant of frontotemporal dementia fvFTD in a population based sample of 85 year olds. Frontotemporal dementias FTDs are a group of neurodegenerative disorders associated with shrinking of the frontal and temporal anterior lobes of the brain.
Workers diagnosed with any frontotemporal disorder can qualify quickly for Social Security disability benefits through the compassionate allowances program or call 1-800-772-1213. Frontotemporal dementia FTD a common cause of dementia is a group of disorders that occur when nerve cells in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain are lost. Common symptoms can include.
Until now no single test is available which allows a reliable differentiation. Inconsistencies in diagnostic criteria small cohorts of patients and neuropsychological assessment may account for such findings. Dementia is a severe loss of thinking abilities that interferes with a persons ability to perform daily activities such as working driving and preparing meals.

It may be the.
Frontal lobe syndrome frontotemporal dementia. Until now no single test is available which allows a reliable differentiation. Frontotemporal dementia FTD a common cause of dementia is a group of disorders that occur when nerve cells in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain are lost. In general changes in the frontal lobe are associated with behavioral symptoms while changes in the temporal lobe lead to language and emotional disorders.
Common symptoms can include. Dementia is a severe loss of thinking abilities that interferes with a persons ability to perform daily activities such as working driving and preparing meals. A representative sample of 85 year olds n 451 in Gothenburg Sweden was examined with a neuropsychiatric examination and a key informant interview performed by an experienced psychiatrist.
To investigate the prevalence of the frontal lobe syndrome FLS and the frontal variant of frontotemporal dementia fvFTD in a population based sample of 85 year olds. An early differentiation of Alzheimers disease AD from frontotemporal dementia FTD is important since these conditions are essentially different regarding prognosis and therapeutical approach. This causes the lobes to shrink.
Although the pathological hallmarks of Alzheimers disease AD and frontal variant frontotemporal dementia fvFTD predict different cognitive patterns many comparative neuropsychological studies showed no difference in the expected cognitive domains. Symptoms include marked changes in social behavior and personality andor problems with language. Frontotemporal dementia FTD is a type of dementia that happens because of damage to the frontal and temporal lobes of your brain.
Frontotemporal disorders are forms of dementia caused by a family of brain diseases known as frontotemporal lobar degeneration FTLD. About 70 percent of cases begin before age 65 so it is a more common dementia among the young old FTD involves degeneration of the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. Workers diagnosed with any frontotemporal disorder can qualify quickly for Social Security disability benefits through the compassionate allowances program or call 1-800-772-1213.
Symptoms of frontotemporal disorders vary from person to person and from one stage of the disease to the next as different parts of the frontal and temporal lobes are affected. Inconsistencies in diagnostic criteria small cohorts of patients and neuropsychological assessment may account for such findings. In this section you will learn the essential facts about FTD.
About 70 percent of cases begin before age 65 so it is a more common dementia among the young old FTD involves degeneration of the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain.
Frontal lobe syndrome frontotemporal dementia. Common symptoms can include. Frontotemporal dementia FTD a common cause of dementia is a group of disorders that occur when nerve cells in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain are lost. Symptoms of frontotemporal disorders vary from person to person and from one stage of the disease to the next as different parts of the frontal and temporal lobes are affected.
In general changes in the frontal lobe are associated with behavioral symptoms while changes in the temporal lobe lead to language and emotional disorders. Frontotemporal dementia FTD is a type of dementia that happens because of damage to the frontal and temporal lobes of your brain. FTD is the diagnosis for about 5 percent of people with major neurocognitive disorders dementia.
Inconsistencies in diagnostic criteria small cohorts of patients and neuropsychological assessment may account for such findings. Dementia is a severe loss of thinking abilities that interferes with a persons ability to perform daily activities such as working driving and preparing meals. Symptoms include marked changes in social behavior and personality andor problems with language.
Its the most common dementia for those under 60 yet its widely misunderstood and too often misdiagnosed. This causes the lobes to shrink. A representative sample of 85 year olds n 451 in Gothenburg Sweden was examined with a neuropsychiatric examination and a key informant interview performed by an experienced psychiatrist.
To investigate the prevalence of the frontal lobe syndrome FLS and the frontal variant of frontotemporal dementia fvFTD in a population based sample of 85 year olds. Frontotemporal dementias FTDs are a group of neurodegenerative disorders associated with shrinking of the frontal and temporal anterior lobes of the brain. These disorders are among the most common dementias that strike at younger ages.
Frontotemporal disorders are forms of dementia caused by a family of brain diseases known as frontotemporal lobar degeneration FTLD. In this section you will learn the essential facts about FTD. Workers diagnosed with any frontotemporal disorder can qualify quickly for Social Security disability benefits through the compassionate allowances program or call 1-800-772-1213.